Today’s ammonia plants use natural gas or other fossil feedstocks both to provide the energy required to power the synthesis process, and as a source of hydrogen. As a result, ammonia production by these methods releases large quantities of CO2.
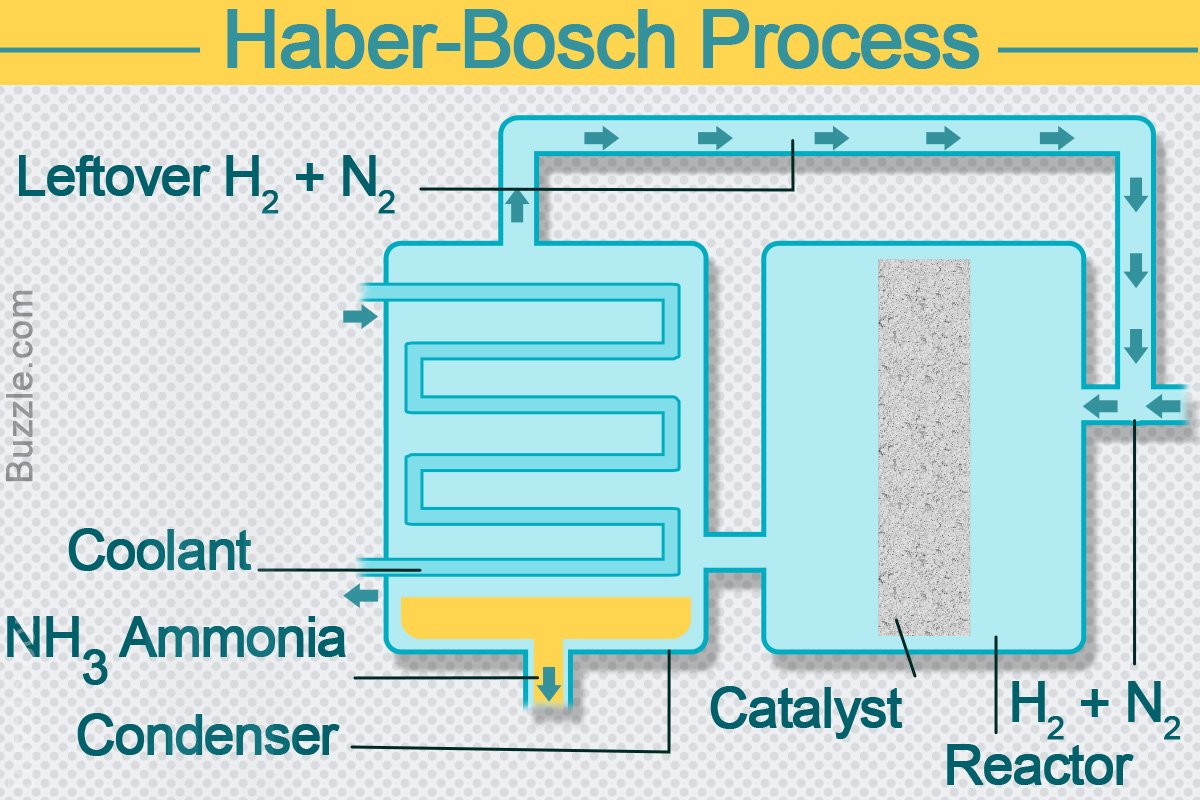 The Siemens Green Ammonia Energy Storage Demonstrator instead uses water electrolysis to provide a hydrogen supply, and extracts nitrogen from the air. The system is designed to use renewable energy to do this, and to combine the two elements in an established Haber-Bosch process to make ammonia. Ammonia produced in this way can be a completely carbon-free and practical bulk energy source.
The Siemens Green Ammonia Energy Storage Demonstrator instead uses water electrolysis to provide a hydrogen supply, and extracts nitrogen from the air. The system is designed to use renewable energy to do this, and to combine the two elements in an established Haber-Bosch process to make ammonia. Ammonia produced in this way can be a completely carbon-free and practical bulk energy source.
This is world’s first demonstrator to show the complete cycle of renewable power, storage as ammonia, and conversion back to electricity.
According to the company, using renewable electricity to make ammonia for fertilizer manufacturing has the potential to save more than 40 million tons of CO2 each year in Europe alone, and over 360 million tons worldwide.
In addition, ammonia can be used as a fuel for gas turbine engines generating electricity at times when renewable energy is not available.
“Carbon-free chemical energy storage – including Green Ammonia – has the potential to work alongside other storage methods such as batteries, and help increase the penetration of renewable power into our energy systems.”






