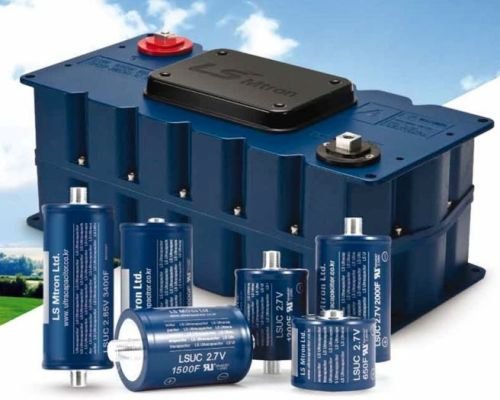
There are batteries and there are supercapacitors. Both do the same thing — store electrical energy. Batteries charge relatively slowly and discharge slowly.
Supercapacitors charge quickly and discharge quickly. Batteries are capable of storing large amounts of energy, supercapacitors are best for storing smaller amounts of energy.
In coming years, supercaps, as they are known, may replace the lead acid batteries currently used by all electric cars to store power for such routine functions as operating door locks, providing interior lighting, and so forth.
Scientists at University College London and the Chinese Academy of Sciences claim they have developed a new flexible graphene-based supercapacitor that can safely charge at high speed, accumulate a record amount of energy, and store it for a long time.
The new supercapacitor uses an innovative multi-layer graphene electrode. It can bend up to 180 degrees without losing its performance and does not require a liquid electrolyte, which minimizes the risk of explosion.
The prototype developed by the research team has an energy density of 88.1 Wh per liter — equivalent to the best lead acid batteries. A typical conventional supercapicitor today has an energy density of about 8 Wh per liter.
In addition, the scientists claim their invention has a power density of 10,000 watts per liter and retains 98.7% of its capacity after 5,000 charge/discharge cycles.
The new device could replace the batteries in smartphones and power wearable internet devices. And because it is much lighter and smaller than a lead acid battery, it could also replace the 12 volt standard battery used in all EVs today.
Reference- Journal Nature Energy, University College London website, Clean Technica, ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY website