There is a tremendous underlying opportunity for an effective delivery of road transport service in India. The advent of electric buses (e-buses) will pave the way for future of efficient mass public transport system.
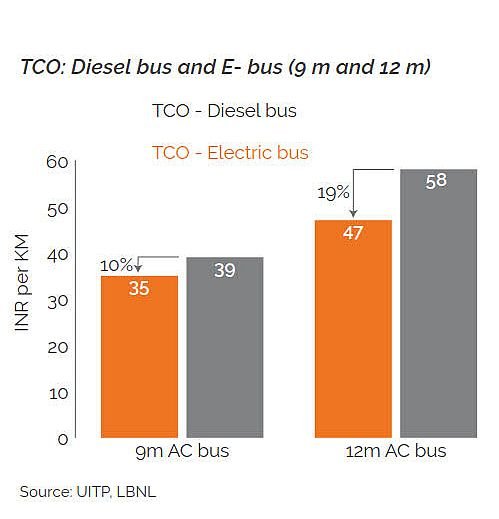
Apart from being cleaner and greener, the major advantage of an e-bus is its extremely low operational and maintenance (O&M) expenditure per unit km.
The Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) of e-buses is 10-20% lesser than that of diesel buses.
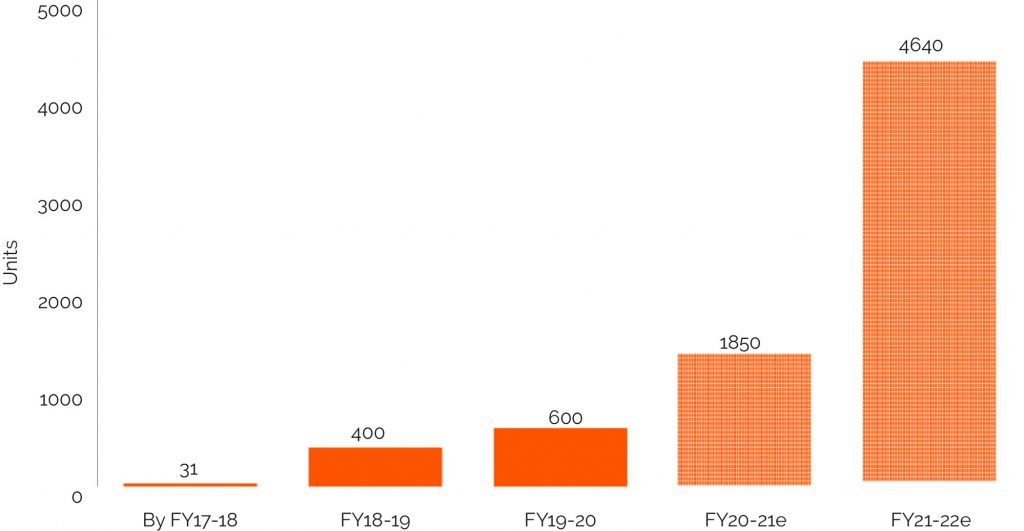
In September 2017, the first commercial e-bus operations began in India in Himachal Pradesh. Since then, the e-bus market has evolved substantially. By March 2020, about 1,031 e-buses were sold across different states and transport undertakings.
As per JMK Research estimates, additional 1850 buses are likely to be sold in FY2021 and around 4640 units in FY2022.
The e-bus market growth is fueled by more than US$1 Bn worth of investment deals forged in the past few years with investors of varied business backgrounds.
The Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises had issued an Expression of Interest (EoI) document in 2019 to invite proposals from states, government departments, transportation departments, and municipal bodies for procurement of electric buses across 40 cities.
The subsidy will be provided under the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid & Electric Vehicles in India or the FAME-II scheme.
The central government will offer subsidies worth Rs 2,500 crore (US$360 million) for the deployment of 5,000 electric buses.

Under the current exercise, a total of 40 cities shall be selected where a subsidy will be distributed for deployment of electric buses based on population.
The timeline set for the complete delivery of all buses has been set at just over 18 months from now.
A number of state transportation agencies have already announced plans to induct electric buses to their fleet. These include agencies in the cities of Mumbai, Bengaluru, Kerala etc.
To keep up with the pace of e-bus induction and deployment onto the public roads, the charging systems and allied-infrastructure must also be enhanced and/or developed systematically to overcome local-specific challenges.
Reference- JMK Research & Analytics Report, Ministry of Heavy Industries website, Economic Times, Business Standard






