Effective water filtration in space is a tough puzzle to solve, space agencies NASA and ESA have turned to nature to solve this issue.
An innovative technology using aquaporins – the membrane proteins that enable transfer of water in all living cells, is now being hailed as the revolutionary solution.
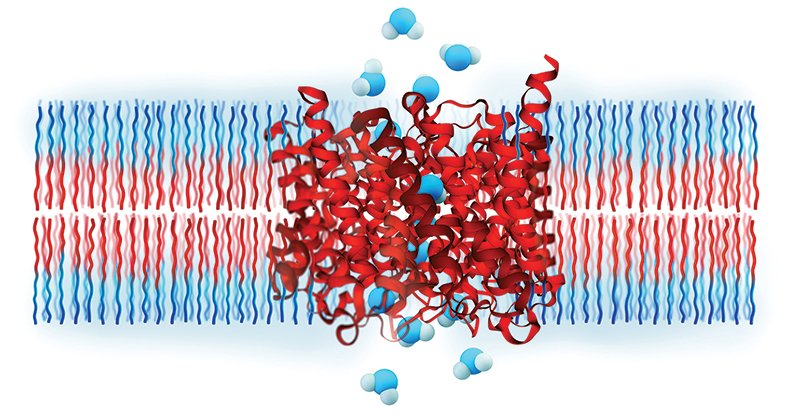
The Danish company, Aquaporin A/S, is responsible for the system based on aquaporins through which plant roots absorb water from soil and human kidneys to filter about 45 gallons of fluid per day.
NASA is interested in the company’s forward osmosis filter, a technology that operates without any energy or outside influence, the space agency explains in a note.

Instead of applying pressure to make the water pass through a filter membrane, forward osmosis acts as a sponge to suck up water from nearby cells through the membrane. The membranes thus have a very low tendency to clog.
This is being tested at NASA’s Ames Research Center. Here sugar water is being used to extract clean water from urine, an application that serves as a life-saver for astronauts in space.

The forward osmosis can handle very dirty water, even eliminating the need for distillation and can filter water about twice as fast as other existing purifiers, due to the proteins’ efficiency,” nearly doubling the water recovery rate.
The prime benefit – the technology allows us to cut down on the great cost of ferrying water into space.
Reference- Aquaporin A/S website & PR, NASA website, Science Alert






