To further integrate renewable energy resources in the grid, India’s Ministry of Power has developed draft rules for procuring power from pumped hydro storage projects. According to a document provided by the Power Ministry, the government plans to build 18 gigawatts of pumped hydro storage capacity. The projects will employ renewable energy to fulfill peak electricity demand.
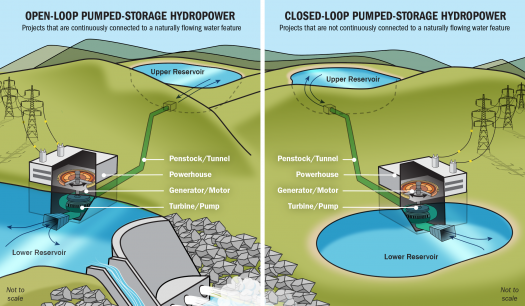
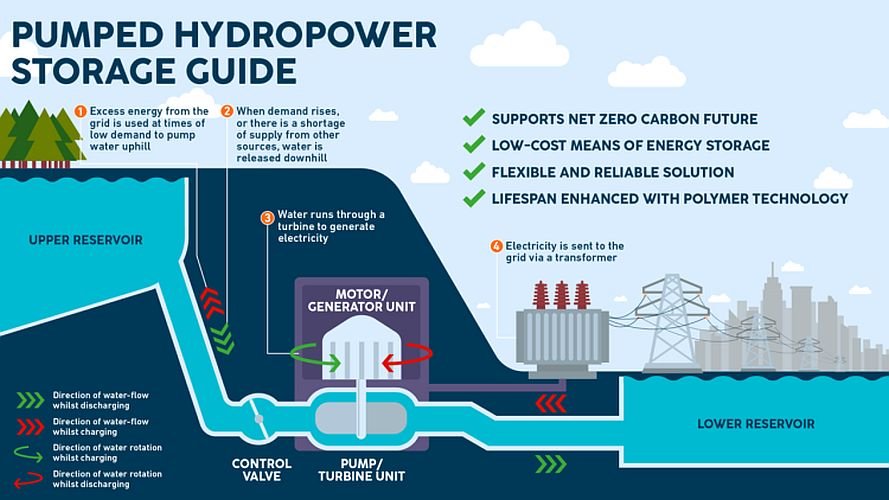
Pumped hydro storage works by pushing water from a lower elevation reservoir to a higher height reservoir. The water is pushed up using low-cost renewable energy during periods of low demand and high generation, such as throughout the day in the case of solar power.
When renewable energy output is curtailed (e.g., after sunset or before sunrise), water held in a reservoir at a higher elevation is utilized to create electricity via turbines. Pumped hydro power storage systems are thus a very efficient method of storing renewable energy (particularly solar electricity) when supply exceeds demand.

According to official statistics, India has eight pumped hydro storage facilities totaling around 4.7 gigawatts but they are currently not being operated in the pumped storage mode.
Four further projects with a total capacity of 2.8 gigawatts are under development, while 26 more with a total capacity of 26.6 gigawatts have been authorized to states. The government believes that the nation has 108 gigawatts of pumped storage potential.
India has just lately begun to issue tenders for the development of storage projects. Despite the fact that battery storage is more adaptable in terms of reaction time and applications, most developers prefer pumped hydro storage. Pumped hydro is a tried-and-true technology that requires little to no imports.
Reference- Economic Times, Ministry Of Power document & website, Mercom India, Business Standard






