Carbon credits act as permits for companies to emit a specified amount of carbon dioxide (CO₂). Each credit allows the emission of one tonne of CO₂. Companies can also generate carbon offsets by removing a tonne of CO₂ from the atmosphere. These offsets are tradable, enabling other businesses to buy them to offset their emissions. This mechanism forms the backbone of carbon markets, designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions cost-effectively.
The potential of carbon markets lies in their ability to curb emissions without hindering economic growth. By treating carbon as a tradable commodity, the system aligns climate action with market principles. Placing a price on carbon incentivizes businesses to lower emissions, translating environmental goals into economic strategies.
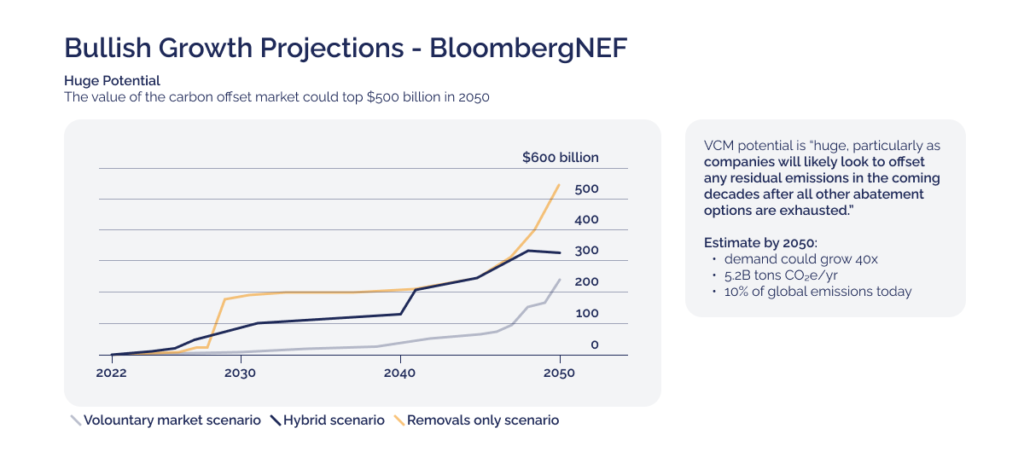
The Rise of Carbon Markets
Carbon markets have grown rapidly in recent years. Projections suggest the market could reach an estimated $100 billion by 2030, demonstrating its expanding significance. This growth highlights the increasing reliance on market-based solutions to address climate challenges.
Benefits of Carbon Markets
One key advantage of carbon markets is their ability to fund climate projects globally, particularly in developing countries. Revenues from the sale of carbon credits often support renewable energy initiatives, forest conservation, and sustainable agriculture. These projects not only reduce emissions but also contribute to economic development and improved living standards in less affluent regions.

Additionally, carbon markets encourage innovation. Companies aiming to lower costs are motivated to invest in cleaner technologies and adopt sustainable practices. Over time, this reduces dependency on fossil fuels and drives the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Challenges and Effectiveness
Despite their potential, questions remain about the effectiveness of carbon markets in significantly reducing emissions. Critics argue that some businesses use carbon credits as a way to delay making meaningful changes to their operations. Ensuring transparency and strict monitoring is essential to prevent misuse and guarantee that credits represent actual emissions reductions.

Conclusion
Carbon markets present a promising yet complex solution to the global emissions challenge. Their success depends on robust frameworks, consistent oversight, and the commitment of all stakeholders. With the market poised to grow further, its impact on climate action will likely expand, making it a crucial tool in the fight against climate change.
References: International Carbon Market Statistics, Climate Finance Report, The Role of Carbon Offsets in Emissions Reductions, UN Report, 2021.






