Vegetation drought is a condition of ecosystem which is affected by climate change and low soil moisture.
Vegetation distribution and growth are significantly affected by changing climate conditions. Understanding the response of vegetation to hydroclimatic disturbances such as droughts is crucial in context of climate change.
The sensitivity of terrestrial ecosystem to drought is difficult to measure because of problems related to drought quantification, variable response of vegetation types and changing climate-vegetation dynamics.
Since, India is hugely dependent on its vegetation and cropland, identifying the impact of droughts on vegetation is essential.
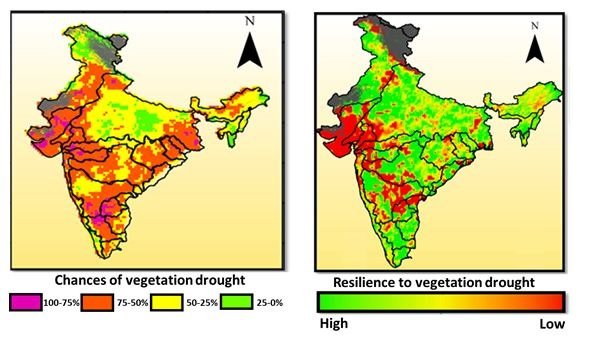
An index based on the data of temperature, rainfall and soil moisture for 29 years from 1982 to 2010 has been developed to understand the effect of climate on vegetation.
According to the study at least half of 16 river basins have been found to be low in soil moisture, due to which the area can be affected most by drought. Area wise, most badly affected river basin was Ganga, since 25 per cent of its area is susceptible to droughts.
Extreme climate events can affect vegetation growth and activity. With increased chances of drought, vegetation ecosystems are likely to become more vulnerable in future.
This study identifies risks associated with vegetation cover(including croplands) and provides insights about resilience under changing climate conditions.
Two-thirds of the country’s total cropland has been found to be sensitive to vegetation drought, which could raise the concern of food security.
This is a ‘India Science Wire’ story; edited by Clean-Future Team






