In the increasingly competitive market for electric vehicles (EV), securing a stable supply of lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries has become critical for all participating car makers.
During the course of the electrification of cars and trucks, Tesla and a few established automotive brands such as BMW and Mercedes-Benz have engaged in the R&D of batteries for the powertrain system.

The degree of involvement varies for these car makers. In the case of Tesla, it has devised its own battery design that improves performance and lowers cost.
Ford also wants to secure its supply lines for electric batteries and is planning to establish an in-house manufacturing for Li-ion batteries. Achieving self-sufficiency in this area will help reduce them in reducing the dependence on the major battery suppliers based in South Korea.

In the companies experience there is no flexibility while manufacturing electric vehicle if one has to procure batteries from outside suppliers, especially as demand continues to grow. So an internal discussion on whether or not to establish in-house electric vehicle battery production is currently on at Ford.
Going forward, Ford will have to present a comprehensive electric vehicle battery strategy soon if it is genuine about having its fossil-fuel vehicles succeeded by battery-electric ones.
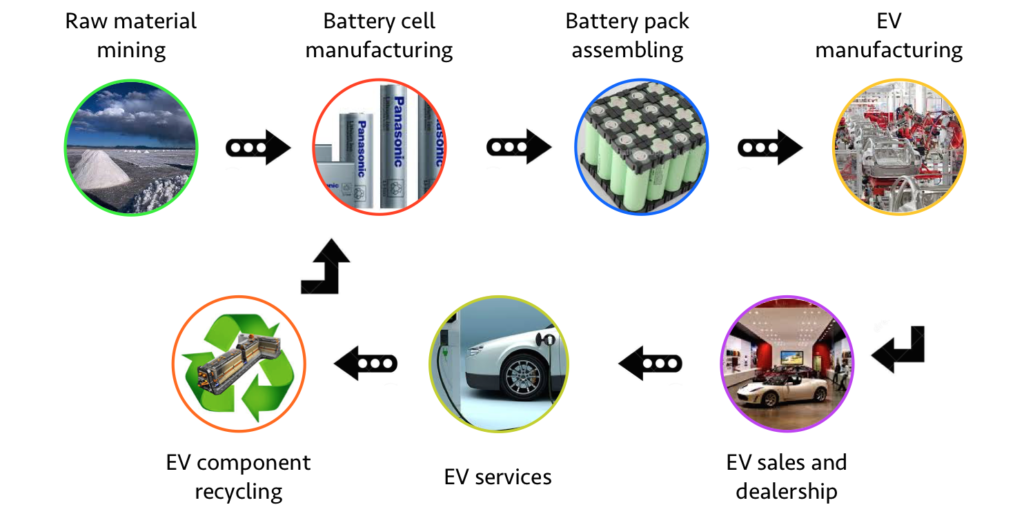
Based on the reporting from media outlets, Ford will most likely form a joint venture with a battery supplier since the car maker lacks the technological expertise in this area.
China’s CATL, for example, has a good chance of becoming a candidate for partnership.
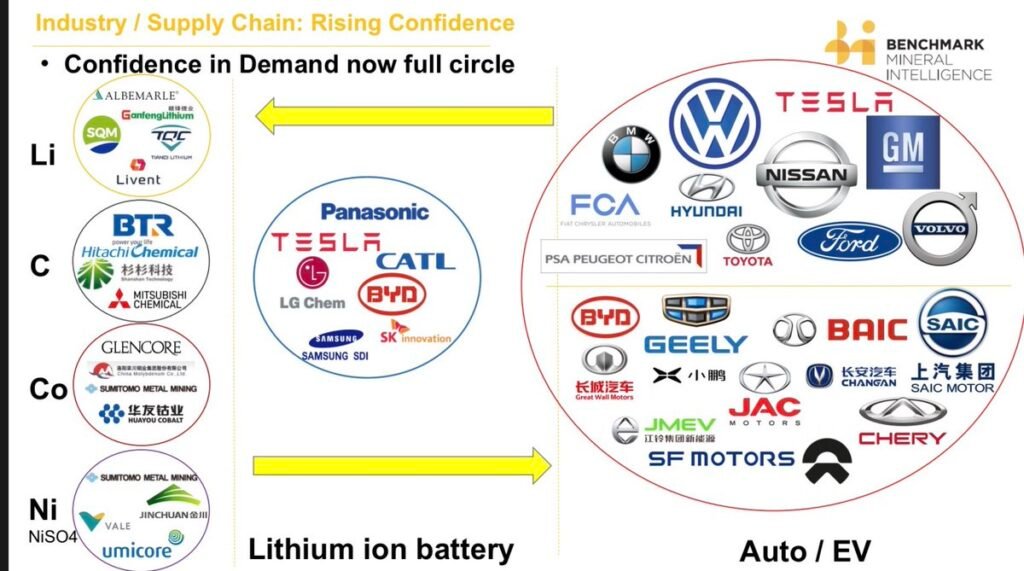
Some car makers have begun in-house development and production, while others have formed joint ventures with battery suppliers. Regardless of strategies, they all must get involved with the battery supply chain.
Tesla, for instance, goes a far upstream as possible, even to the point of mining its own lithium.
Reference- Clean Technica, Forbes, Ford Online PR, Motor World






